
Project finance
What is Project finance?
Project finance is a structured finance solution. It is used to pay for the construction and operation of projects such as wind farms, hydroelectric dams or highways. It is long-term financing. Debt-repayment is mainly based on cash flows generated from the completed project. Project financing includes infrastructure financing as well as PPPs (Public Private Partnerships).
A Project finance usecase
Let's take the case of a company that wants to build and operate a highway. Instead of taking on debt directly, this company will create a legal entity called a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), into which it will inject cash in the form of capital. This makes the company the sole owner/shareholder of the SPV – but it is actually the SPV that will be borrowing from banks in order to finance the project. Once the project is built, it is the financial results (cash flows) from the project that will enable repayment of the debt.
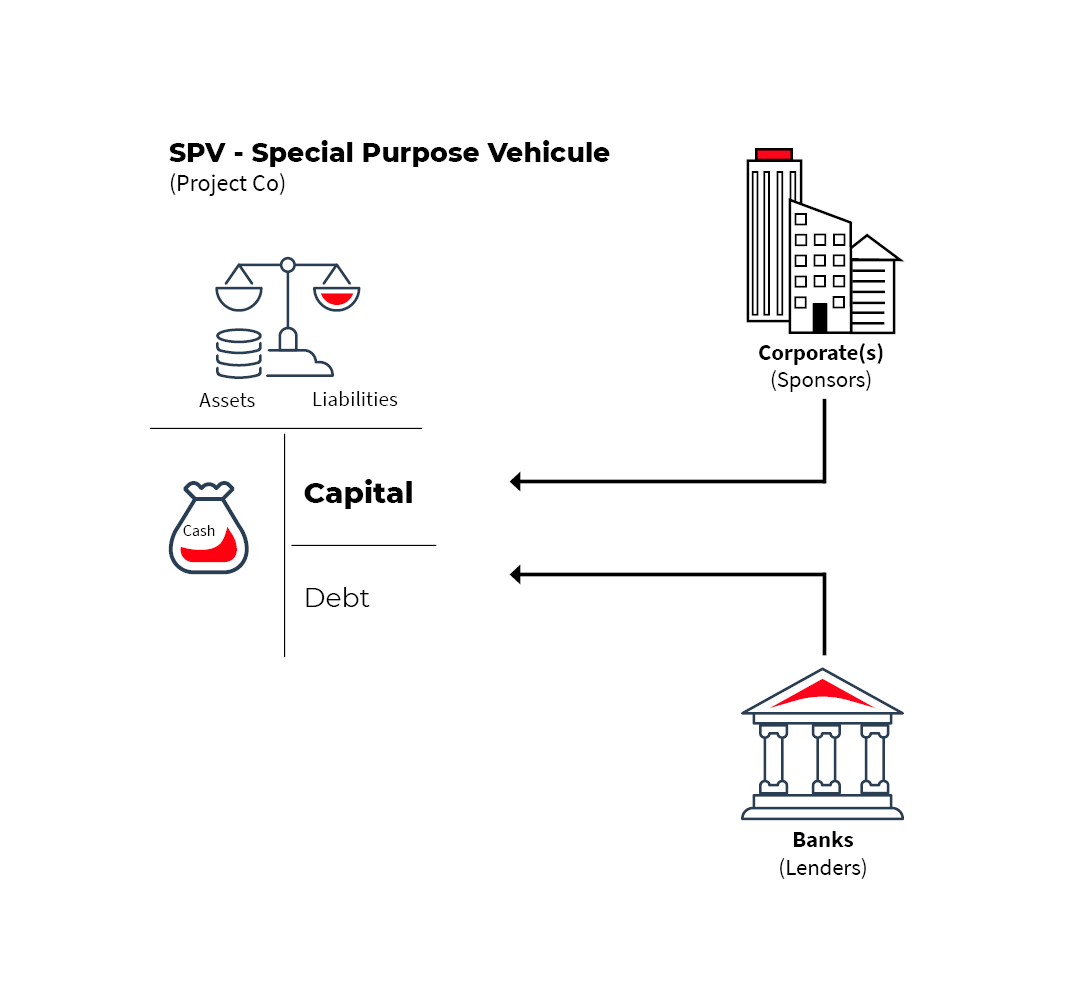
What are the advantages of Project finance for a company?
For the company sponsoring the project, the advantages are multiple:
- reduces the risks in in the event the project fails, since any losses are limited to the amount of capital brought into the SPV (contrary to a direct loan taken out by the company);
- enables the financing of large projects with minimal investment, since the debt represents a significant part of the financing and the client(s) only contributes the capital;
- distributes risk and expertise among different stakeholders since an SPV can be owned by several companies
- the debt is generally provided by several banks or institutional investors in order to mutualize/share the risks.
Role of the bank
The bank acts as an advisor. It helps to structure the project by defining the risks of the project and the means to cover them, both at the financial level (definition of the amounts of capital and debt, definition of the levels of senior and mezzanine debt) and at the legal level. The bank finances and recruits additional investors to help finance the project (syndication). It can also act as an agent, i.e., as an intermediary between the client and the project's lenders.
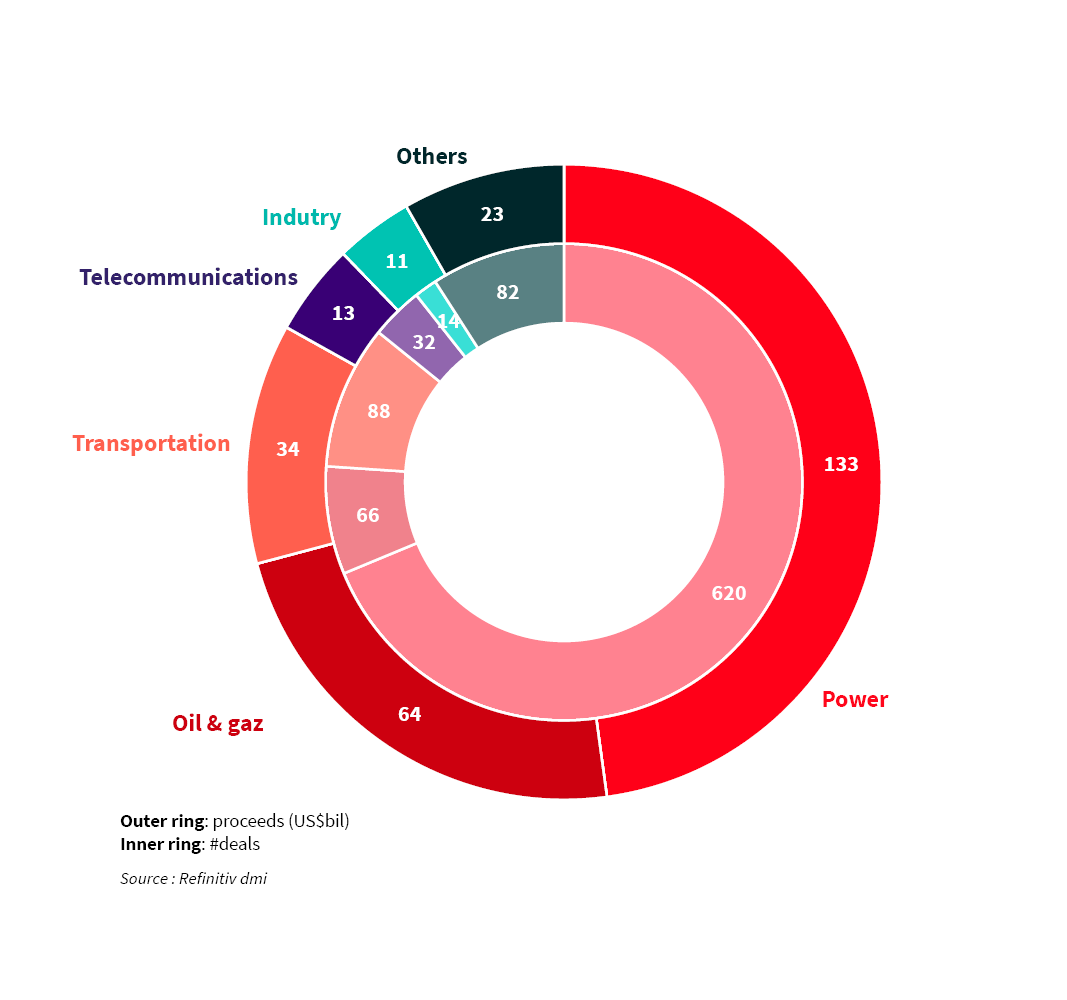
Project finance: for what sectors?
Our latest news and insights

Societe Generale has been distinguished at the Real Estate Capital Europe Awards, earning three top accolades that...

What if our biggest edge in an AI world isn’t more data—but better learning

Societe Generale has demonstrated its leadership in project and infrastructure finance, earning several recognitions...
